

WHAT IS SEARCH ENGINE MARKETING
Definition: SEM uses paid ads on search engine results pages (SERPs) to boost visibility for specific keywords.
Keyword Bidding: Advertisers bid on keywords users enter in search engines (e.g., Google, Bing) related to products or services.
Ad Placement: Bidding helps secure higher positions in search results.
Ad Formats:
Product Listing/Shopping Ads: Visual, product-focused ads showing details like price and reviews at a glance..
Pay-Per-Click (PPC): Advertisers pay only when users click the ad.
Text-Based Ads: Simple, keyword-driven text ads.
Why Search Engine Marketing (SEM) Matters

- Effective Growth Tool: SEM is a powerful way to expand your business in a competitive market.
- High Visibility: Helps your brand stand out among millions of competitors.
- Promotes Products Efficiently: One of the best strategies to boost product visibility and drive business growth.
SEM Keyword Research
Identify Relevant Keywords: Focus on terms potential customers might use to find your products or services.
Use Tools: WordStream’s Free Keyword Tool helps generate keyword ideas.
Key Insights: The tool provides data on search volume and competition for each keyword, aiding in campaign planning.
The Search Engine Marketing Ad Auction
Myth: Only large budgets succeed in SEM.
Reality: Success isn’t solely budget-dependent, as ads must pass through an ad auction.
Google Ad Auction: Determines ad placement based on factors beyond budget, including ad quality and relevance.
How the Ad Auction Works
Trigger: Happens each time a search query is entered.
Bidding: Advertisers bid on specific keywords and set a maximum cost-per-click.
Ad Entry: Ads enter the auction if the bid keywords match a user’s search query.
Placement: Google determines ad placement based on bid and keyword relevance.
How Ads ‘Win’ the Ad Auction
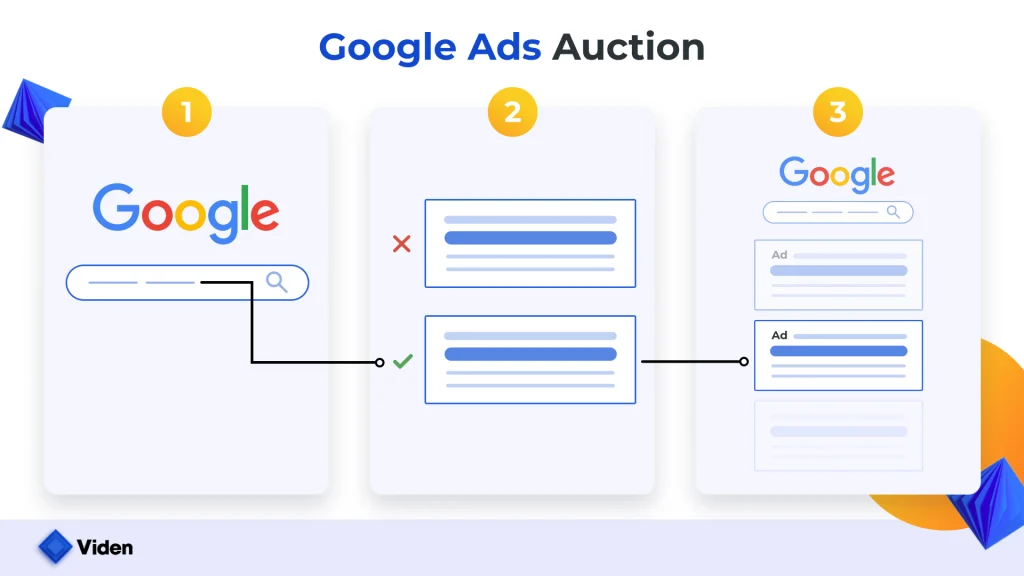
Selective Ad Display: Not all ads show; only those with enough relevance and commercial intent appear.
Primary Factors:
- Maximum Bid: Highest amount you’re willing to pay per click.
- Quality Score: Rating of ad quality and relevance.
Ad Rank: Combination of Maximum Bid and Quality Score, used to determine ad placement on the SERP.




